Ph.D. Computer Science (Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence)
2018 - 2024
- Advisor: Dr. Xiaoli Fern
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for molecule generation
aliraza@meta.com
Phone
+541-360-9372
Location
California, USA
Who/What am I?
I am a research scientist [machine learning] at Meta (Facebook/Instagram).
Fei-Fei Li, Director of the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab, once said at the WIRED25 Summit:
"What’s really important is putting humanity at the center."
Whether developing the first-ever optical character recognition (OCR) system for Urdu—the national language of Pakistan, written in Perso-Arabic Nastalique script—or creating a distributed, GIS-based real-time syndromic surveillance system during Pakistan's dengue epidemic, I have consistently dedicated myself to projects and research that benefit human society, the natural environment, or the synergy between the two.
I am a tech enthusiast who spends time learning about emerging technologies. Beyond work, I enjoy street photography as a hobby. I also play badminton and cricket, and I am currently learning to play the guitar. I like to think of myself as a good singer—though those who have heard me might disagree, and they’re probably right.

• Working with the IFR (In‑Feed recommendations) team
Using machine learning and deep learning to design graph neural networks (GNNs) to process graph data, make predictions, and explain those predictions. Worked on research projects related to computer vision and recommendation systems
Worked with the IFR (In-Feed recommendations) team to build implicit interests based on user engagements to recommend unconnected content
Worked on optimizing power utilization in data centers using non-deterministic heuristics
Worked with the Pre-processing team to develop an Optical Character Recognition (OCR) System using Java for Urdu (national language of Pakistan) Perso-Arabic Nastalique writing styles.
Worked with the C-SVAR team to develop a centralized disease surveillance system based on dis-tributed network of hospitals to address the infectious disease surveillance challenges in Pakistan
Some of my highlighted projects.
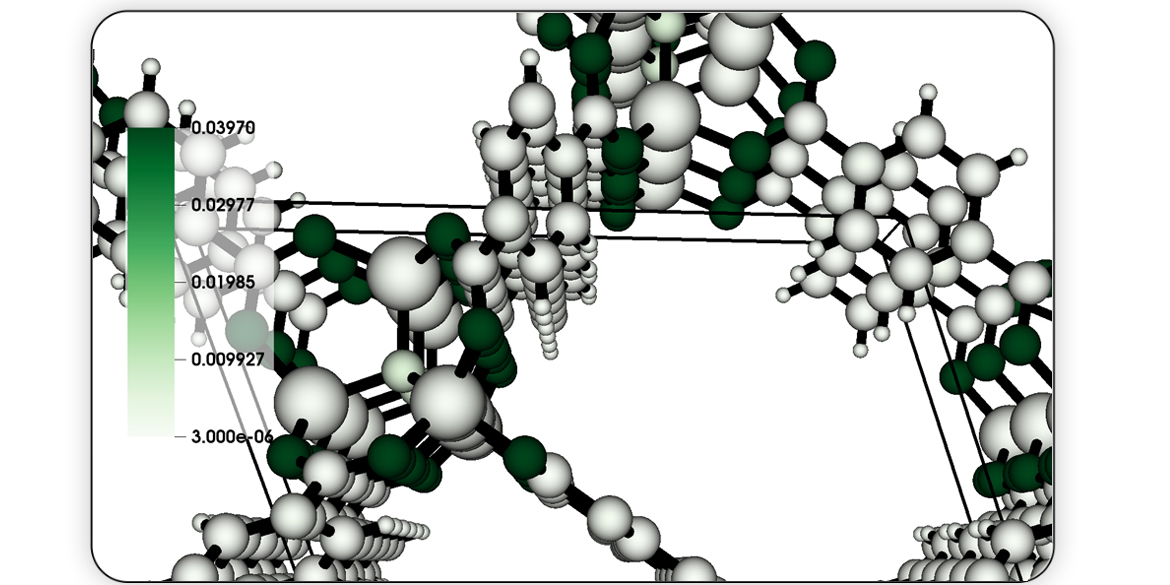
Metal-organic framework (MOFs) are nanoporous materials that could be used to capture carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of fossil fuel power plants to mitigate climate change. In this work, we design and train a message passing neural network (MPNN) to predict simulated CO2 adsorption in MOFs. Towards providing insights into what substructures of the MOFs are important for the prediction...
Read More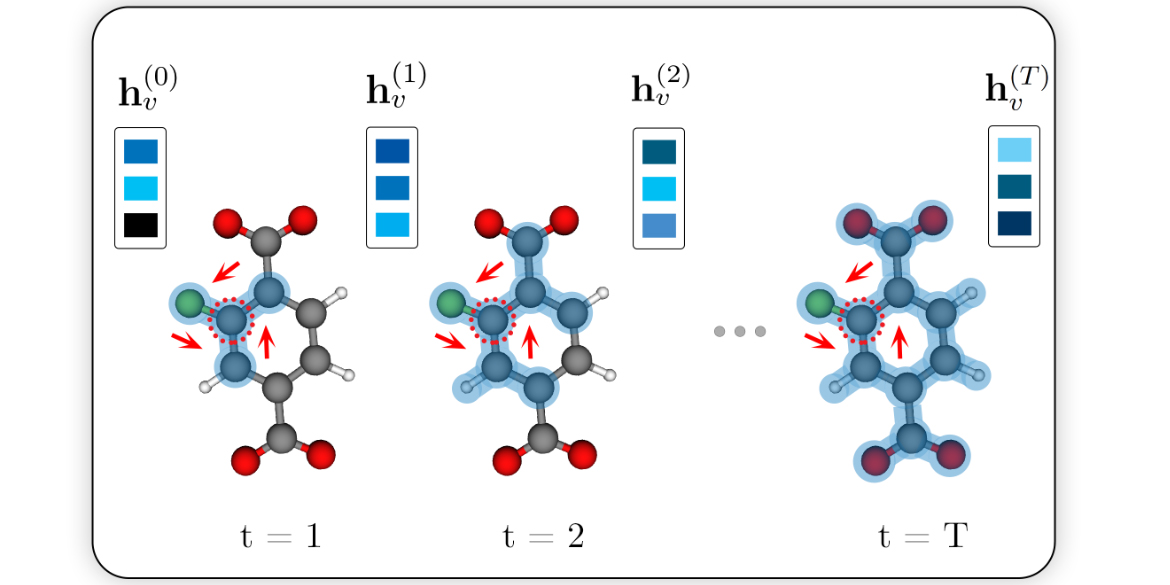
Virtual screenings can accelerate and reduce the cost of discovering metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for their applications in gas storage, separation, and sensing. In molecular simulations of gas adsorption/diffusion in MOFs, the adsorbate-MOF electrostatic interaction is typically modeled by placing partial point charges on the atoms of the MOF. For the virtual screening of large libraries of MOFs...
Read More
Learning efficient latent space representation of the input space in an unsupervised manner has been a major research topic in machine learning. The latent representation can be used not only for dimensionality reduction by capturing the hidden structure of the data, but it can also be used to generate new data, either by interpolation or by sampling. Periodic images consist of infinite copies of their unit cells. A unit cell contains enough information to describe the whole image. Latent representations of these unit cells can correspond to the information-rich fingerprint of the whole image that encodes its salient features and can be used for features reduction, characteristic prediction, and synthesis of new images with given properties. However, a single periodic image can have a large number of unit cells and encoding them to a single point in the latent space is not trivial. In this paper, we propose a framework to encode periodic images while taking care of the boundary effect. We evaluate our approach with the vanilla autoencoder.
Read More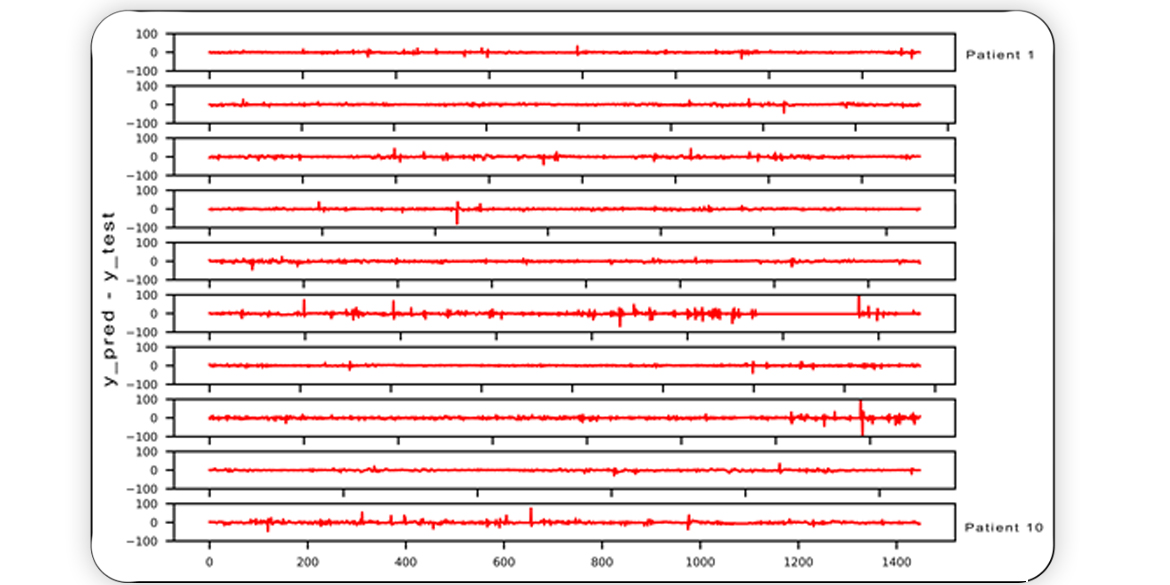
Predicting future blood glucose levels permits diabetes patients to take necessary action before imminent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. We used a deep learning network including long-short-term memory (LSTM) in multi‑task learning of blood glucose from time‑series data.
Read More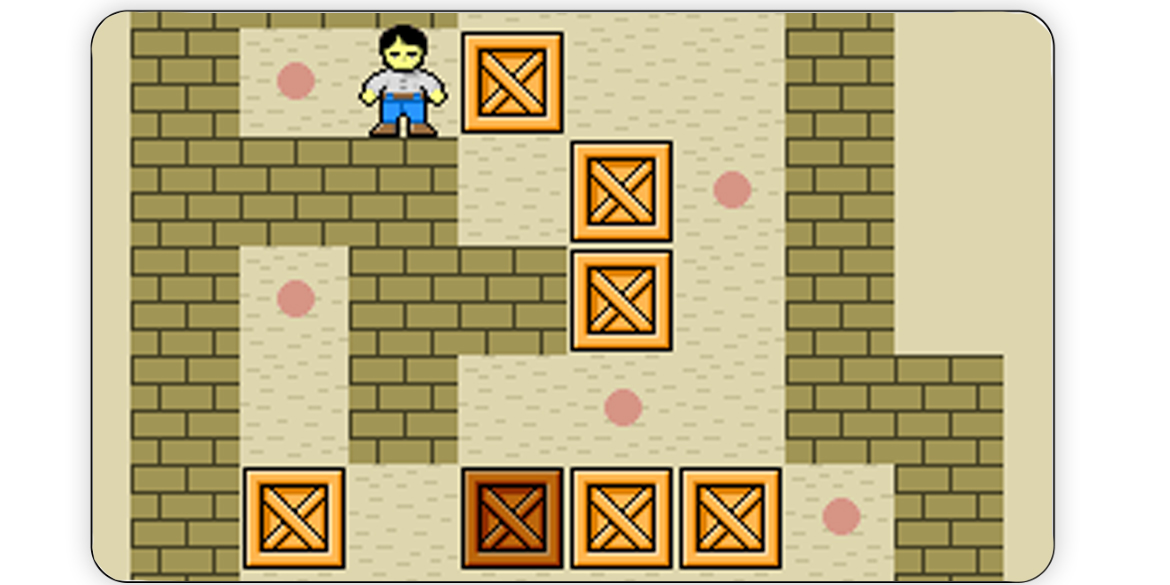
Artificial intelligence (AI) research has developed an extensive collection to methods to solve state-space problems. These techniques have been successful for a wide range of games like chess and checker. Sokoban is a simple puzzle game yet it has variety of problem instances with wide range of complexity from easy to extremely difficult. Furthermore, the powerful restriction of actions makes it an interesting benchmark for comparing different AI search algorithms. In this work, we evaluate six different search algorithms; Depth First, Breadth First, Uniform Cost, A*, and Monto Carlo search algorithms. Furthermore, we explore different heuristic functions. We use a wide range of problem instances for evaluation purposes.
Read More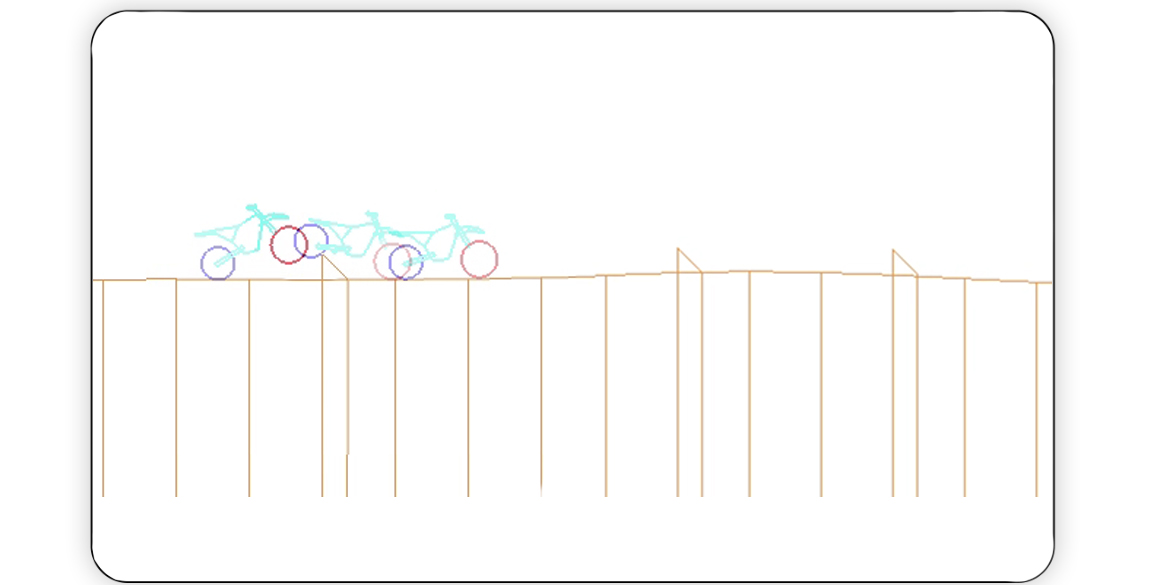
Reinforcement learning(RL) techniques are a sub-field of machine learning approaches, in which an agent tries to learn the dynamics of an environment by trial and error by having interaction whithin the environment. The goal of the agent is to get the best feedback from the environment, which is defined as reward. Given the state of the environment, agent takes an action to maximize the expected future reward. The function that maps states to actions are called policies. However, it is difficult for the agents to learn a general policy that applies across similar environments. Furthermore, they do not get reasonable performances on the same environments of varying difficulty level. To address these problems, we introduce a new pipeline for generating environments with varying difficulty levels to improve the agents’ performances.
Read More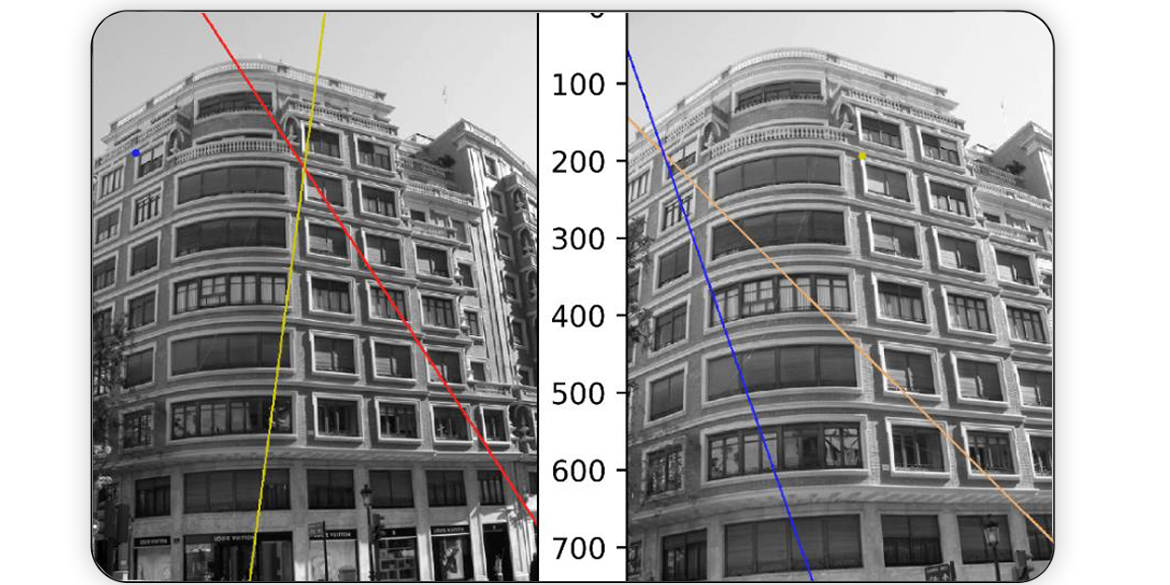
In this work, we used manual points and SIFT keypoints detector. more detail coming..
Read More
Worked with the Pre-processing team to develop an Optical Character Recognition (OCR) System using Java for Urdu (national language of Pakistan) Perso-Arabic Nastalique writing styles.
Read More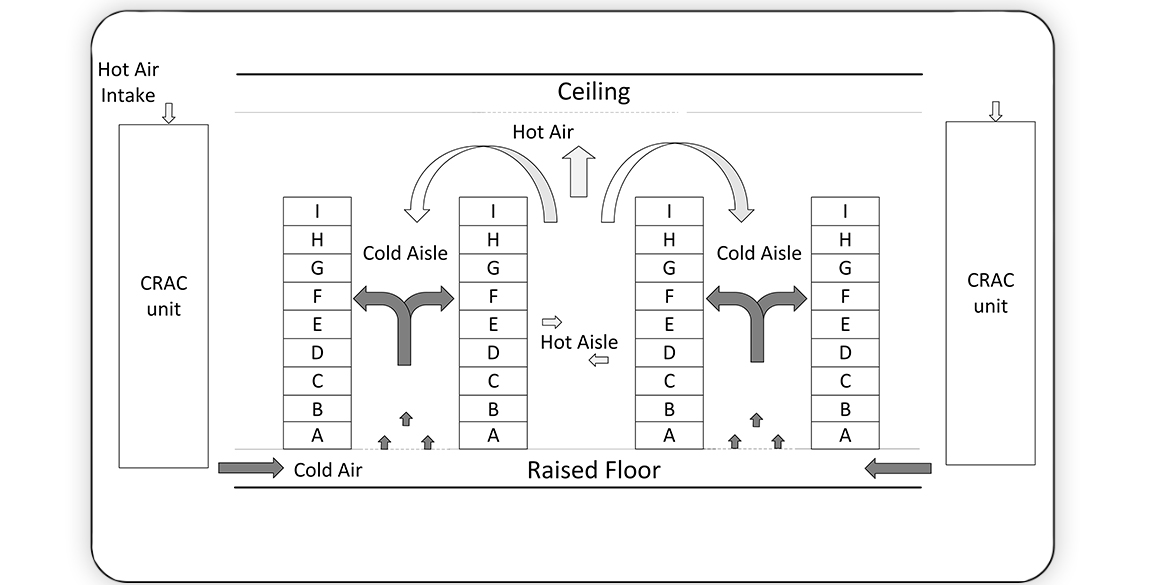
Cloud computing has evolved as the next generation platform for hosting applications ranging from engineering to sciences, and from social networking to media content delivery. The numerous data centers, employed to provide cloud services, consume large amounts of electrical power, both for their functioning and their cooling. Improving power efficiency, that is, decreasing the total power consumed, has become an increasingly important task for many data centers for reasons such as cost, infrastructural limits, and mitigating negative environmental impact. Power management is a challenging optimization problem due to the scale of modern data centers. Most published work focuses on power management in computing nodes and the cooling facility in an isolated manner. In this paper, we use a combination of server consolidation and thermal management to optimize the total power consumed by the computing nodes and the cooling facility. We describe the engineering of an evolutionary non-deterministic iterative heuristic known as simulated evolution to find the best location for each virtual machine (VM) in a data center based on computational power and data center heat recirculation model to optimize total power consumption. A “goodness” function which is related to the target objectives of the problem is defined. It guides the moves and helps traverse the search space using artificial intelligence. In the process of evolution, VMs with high goodness value have a smaller probability of getting perturbed, while those with lower goodness value may be reallocated via a compound move. Results are compared with those published in previous studies, and it is found that the proposed approach is efficient both in terms of solution quality and computational time.
Read More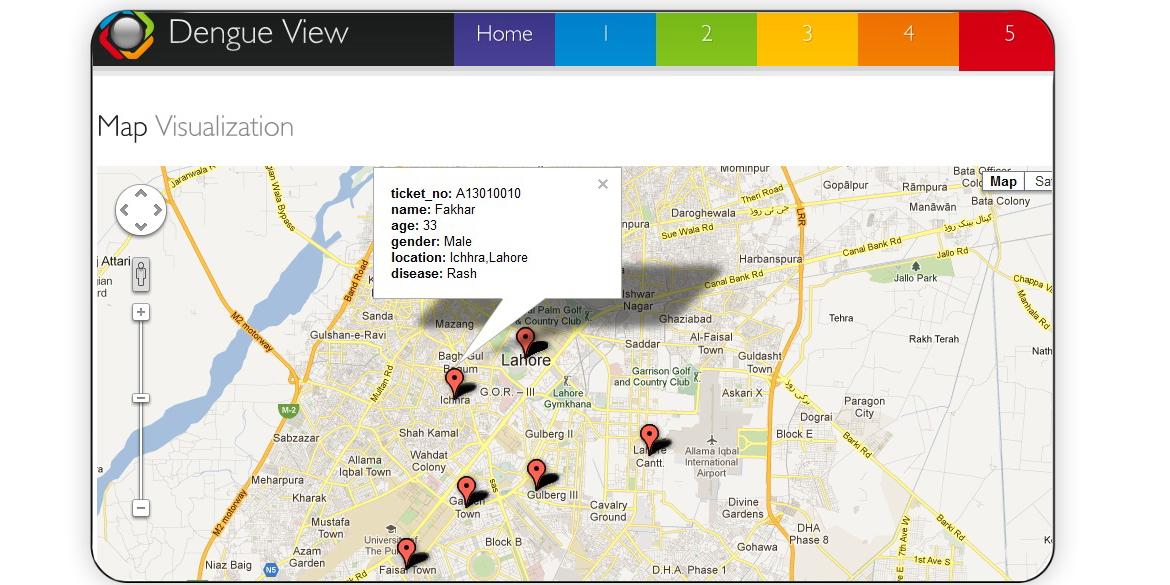
Each year, millions of Pakistanis are exposed to, and infected with, deadly pathogens including hepatitis, tuberculosis, malaria, and now dengue. Lack of a robust infrastructure for the timely collection, reporting, and analyses of Dengue Epidemic (DE) data undermines epidemic preparedness and poses serious health challenges to the general public in Pakistan. In fact, monitoring of the outbreak and response to any natural or man-made infectious disease (ID) is non-existent in the country due to insufficient resources, poorly trained staff, and inadequate health policy implementation. We developed a distributed GIS-based real-time syndromic surveillance system that allows collection, communication, analysis, and visualization of DE data. In the Dengue-View project, we developed a dengue surveillance, analysis, and visualization tool-set for the whole of Pakistan by employing robust and novel infrastructure to facilitate the exploration of spatio-temporal datasets that will be collected in real-time from the emergency departments (EDs) of the corresponding hospitals. The proposed system and the capabilities developed are expected to play a vital role during future dengue epidemic outbreaks (rather, any ID outbreaks) and help efficient use of the scarce resources of different governmental organizations and hospitals. Dengue-View will allow real-time monitoring of health care conditions, related to the dengue epidemic, in collaboration with the partnering hospitals. Doctors, researchers, and officials of the SERCs and the PHD, GoP, can run different filters and get a better picture of the situation and plan different preventive measures needed like insecticide spraying in certain regions or providing specific vaccination
Read MoreFeel free to reach out.
Email:
aliraza at meta dot com
08ali155 at google dot com
Address:
California, USA